Define how AI Decisioning is configured across workspace, agent, and message levels.
| Audience | Platform admins (workspace settings), Marketers (agent and message settings) |
| Prerequisites |
|
What you'll learn
- Workspace-level configuration — Set global defaults
- Agent configuration — Configure targeting, goals, and delivery
- Message configuration — Define tags, goals, and catalog recommendations
Overview
Configuration in AI Decisioning spans multiple levels to balance global guardrails with agent-level strategy and message-level relevance.
Configuration is structured as:
- Workspace configuration – Shared defaults and constraints that apply across all agents, including the global user population, time zone handling, channels, scheduling limits, and Insights inputs.
- Agent configuration – Controls how individual agents operate within those boundaries, including eligibility, goals, scheduling rules, and suppression logic.
- Message configuration – Fine-tunes how specific messages behave using tags, goals, collections, and advanced delivery controls.
Together, these layers determine which users can be evaluated, when messages can be sent, and how learning occurs based on delivery and performance data.
Workspace configuration
Use workspace configuration to define the global defaults and constraints that apply across all agents in your Hightouch workspace.
How to access workspace configuration
- Open the Hightouch app at https://app.hightouch.com.
- Navigate to AI Decisioning in the left-hand navigation.
- Select Configuration.
General
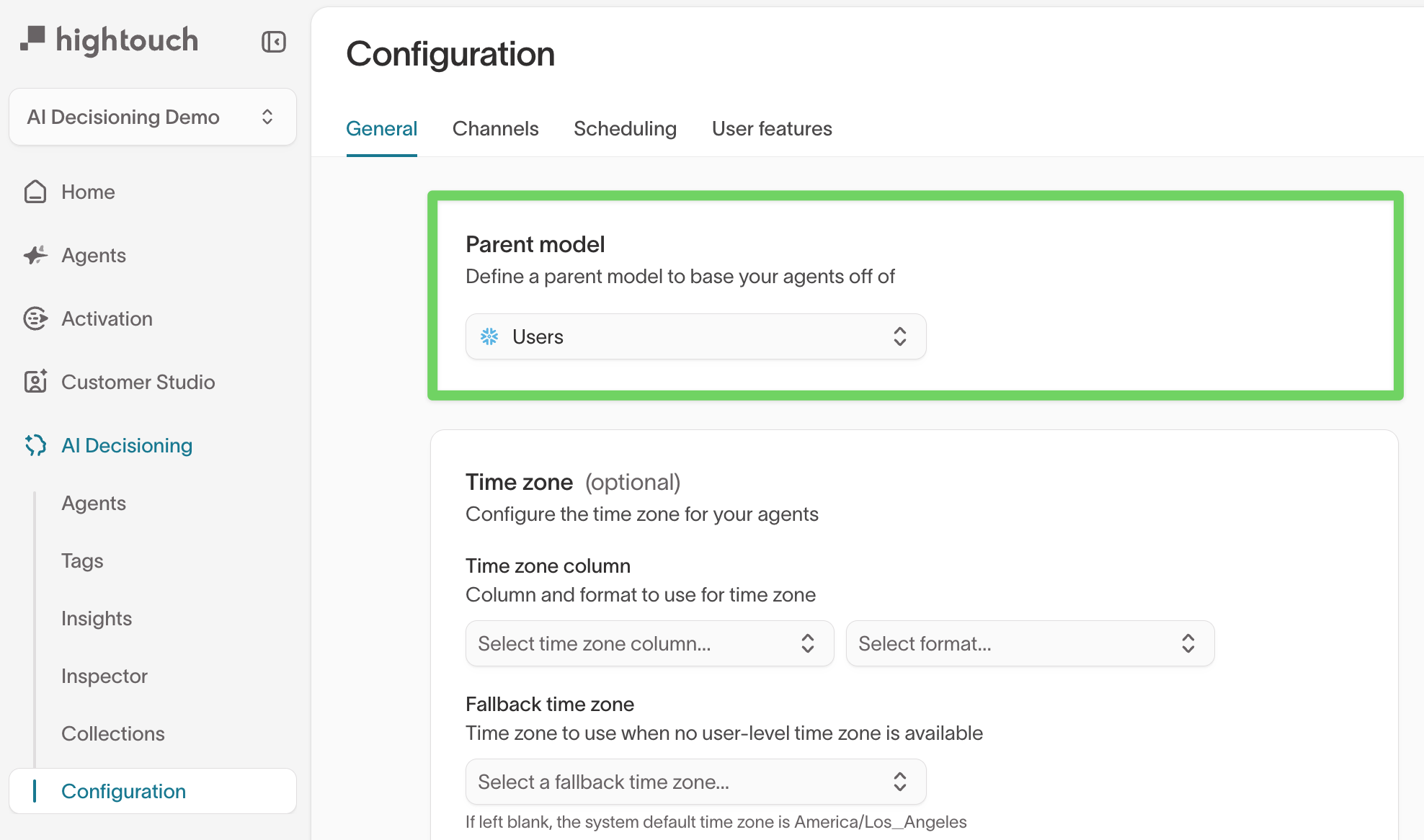
Parent model (global user eligibility)
The parent model defines the complete set of users that AI Decisioning can consider across all agents. Every agent audience is evaluated within this model.
- Recommended: Use a broad, inclusive model such as
Users - Users not included in the parent model are never eligible for AI Decisioning actions, even if they match agent-level criteria
Learn more about defining parent models and preparing your data schema: Prepare data for AID →
Time zone defaults
Configure time zone defaults to evaluate scheduling rules, frequency limits, and quiet hours using each user’s local time.
You can configure:
- User time zone field – A field from the parent model (for example,
user.time_zone) formatted as a UTC offset (such as+09:00) or IANA string (such asAmerica/Los_Angeles) - Fallback time zone – Used when a user does not have a valid time zone value
Time zone settings are used to personalize send windows and enforce quiet hours in each user’s local time.
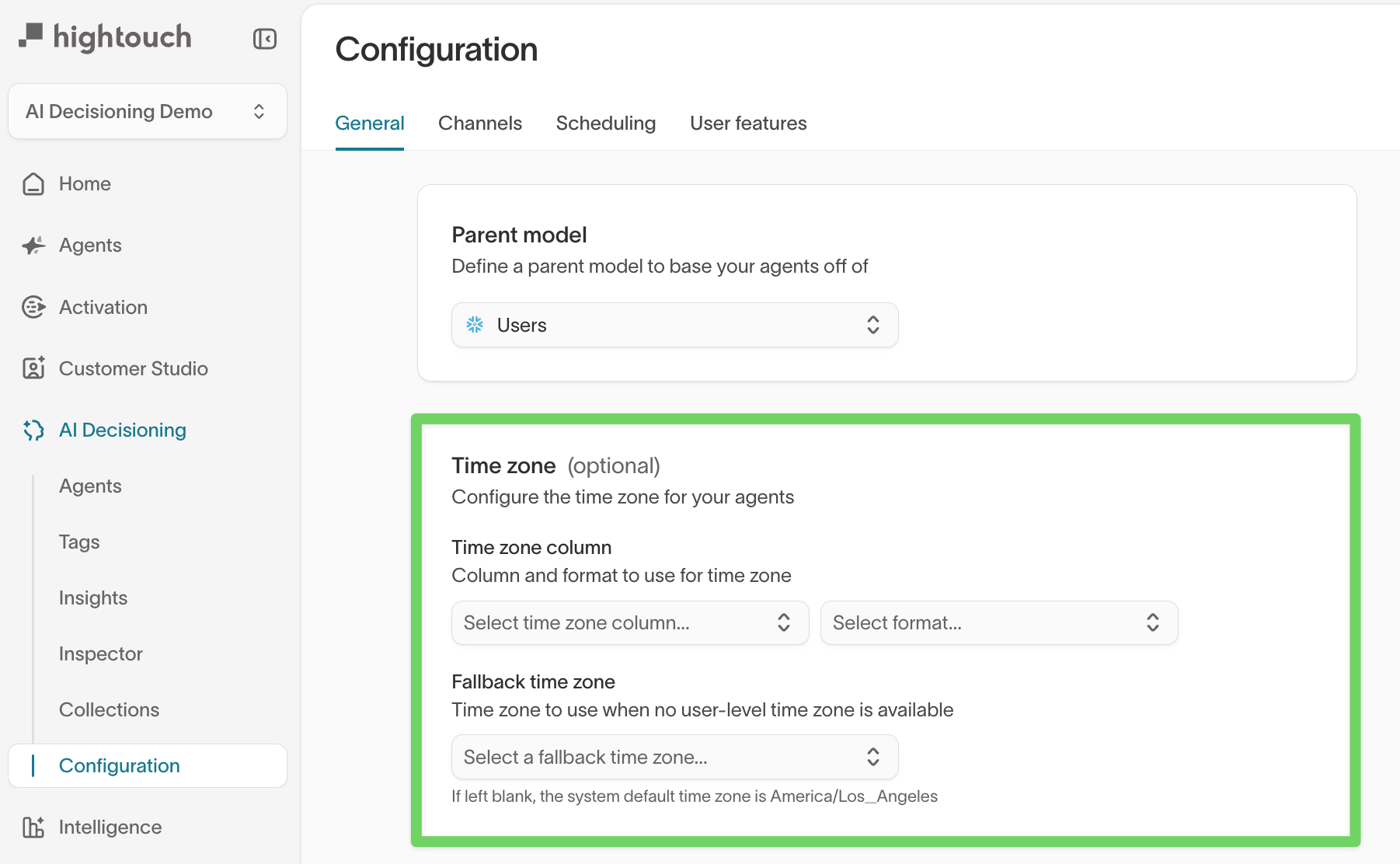
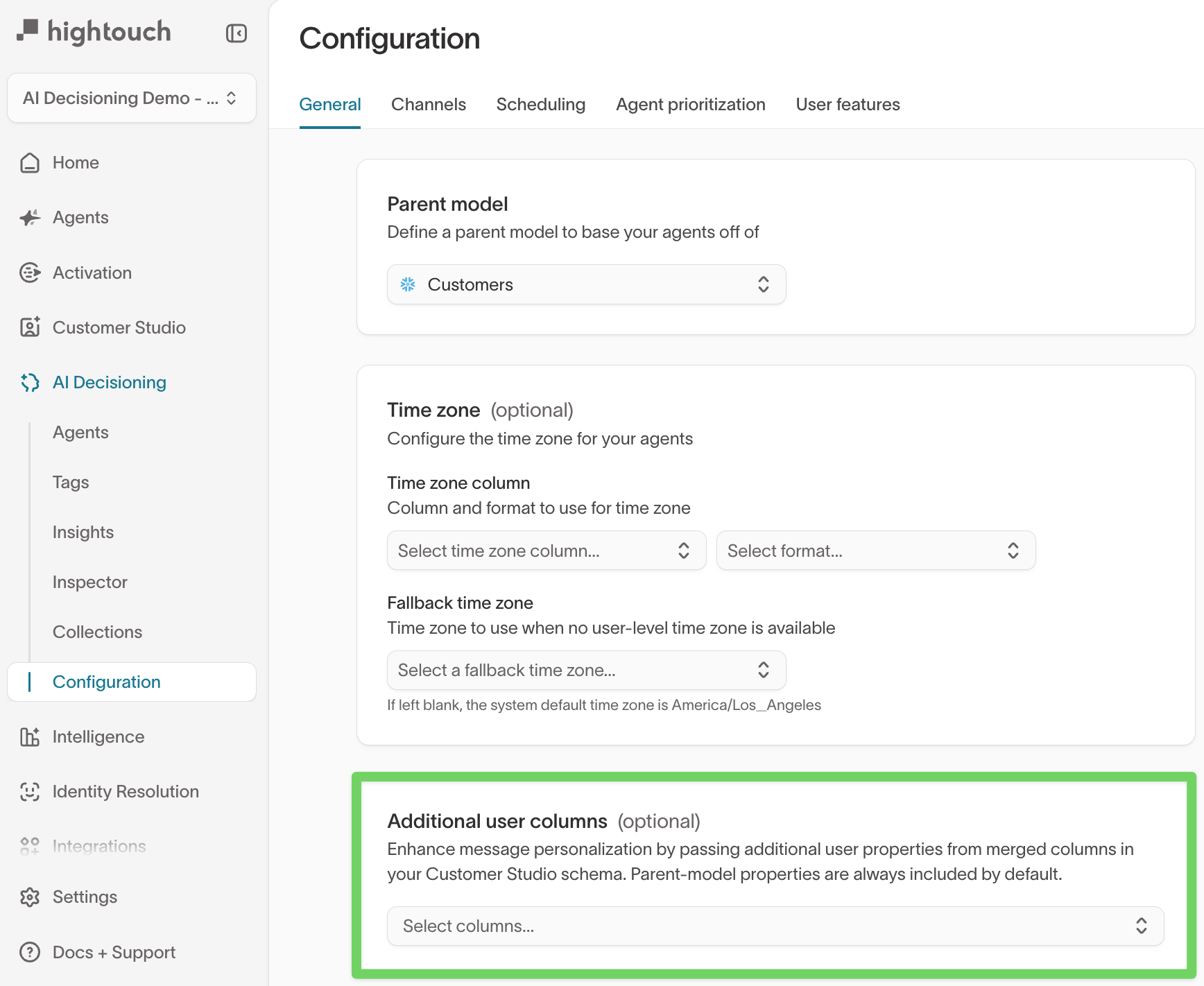
Additional user columns
Additional user columns allow you to expose merged or derived fields from your data model for use in personalization and Insights. These columns extend the parent model without duplicating schema structure.
Channels
Channels determine which messaging destinations are available to AI Decisioning agents and messages.
Supported channel types typically include:
- SMS
- Push notifications
- In-app messaging (inbox, popups, etc.)
- Custom destinations, such as S3 buckets or internal APIs
Active channels
Add channels to make them available when configuring messages within agents.
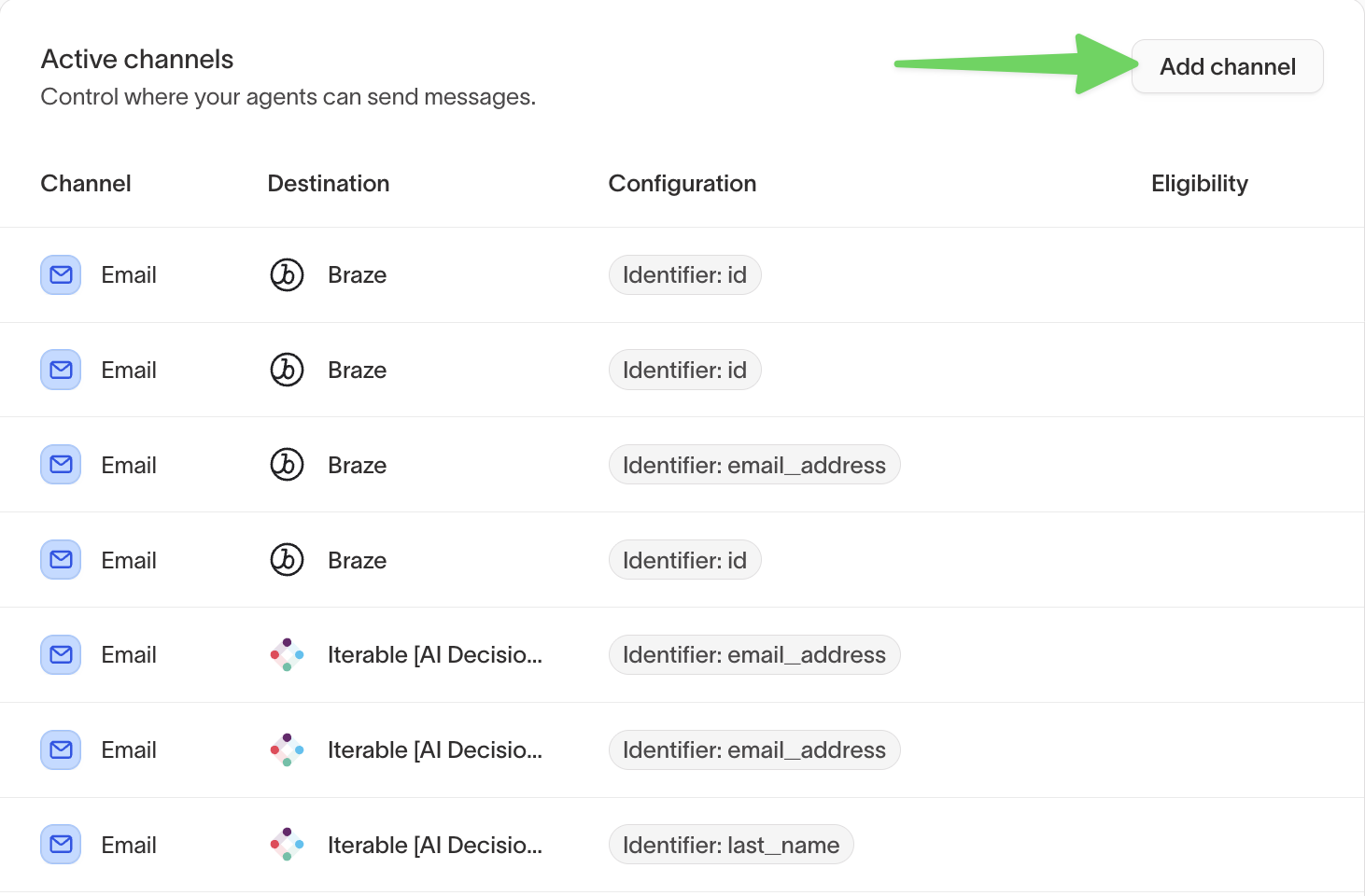
Channel-level eligibility
Channel-level eligibility restricts which users are allowed to receive messages through a specific channel.
Common use cases include:
- Enforcing opt-in requirements for SMS or push
- Applying region-based or compliance-driven delivery rules
Channel-level eligibility is evaluated in addition to agent- and message-level eligibility.

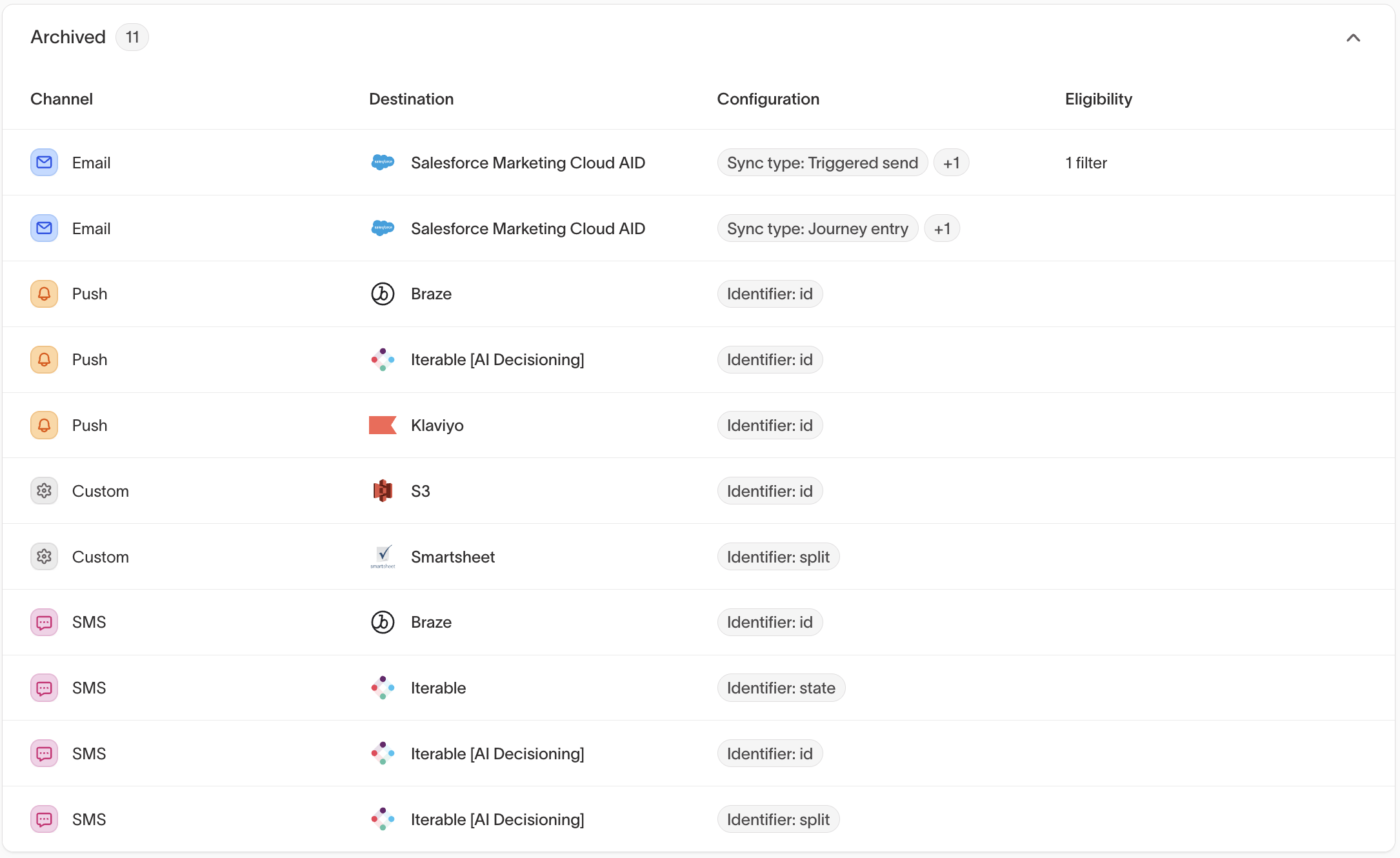
Archived channels
Archived channels are unavailable for new messages but remain visible for historical reference.
Scheduling
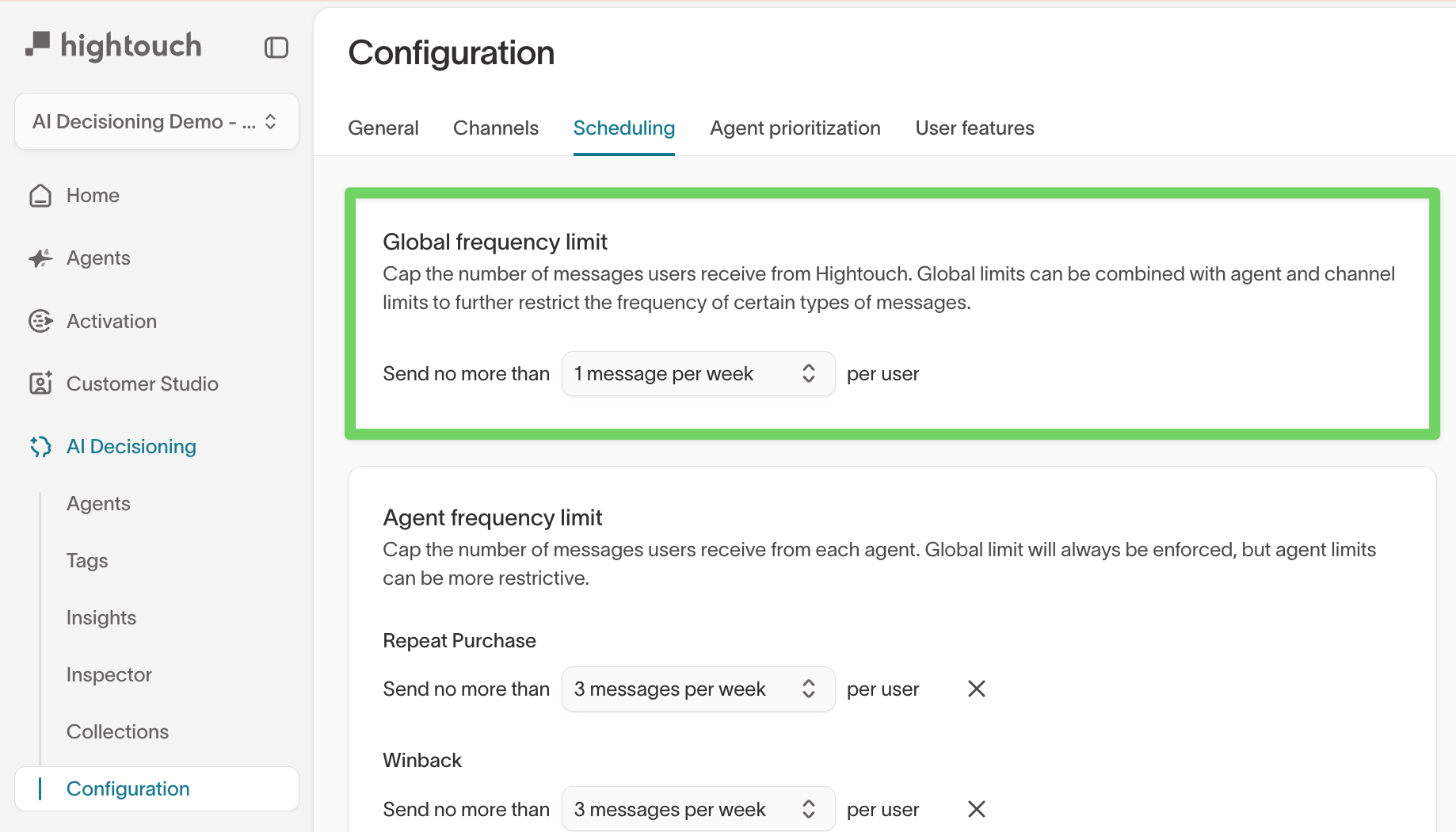
Global frequency limit
The global frequency limit caps the total number of messages a user can receive across all agents.
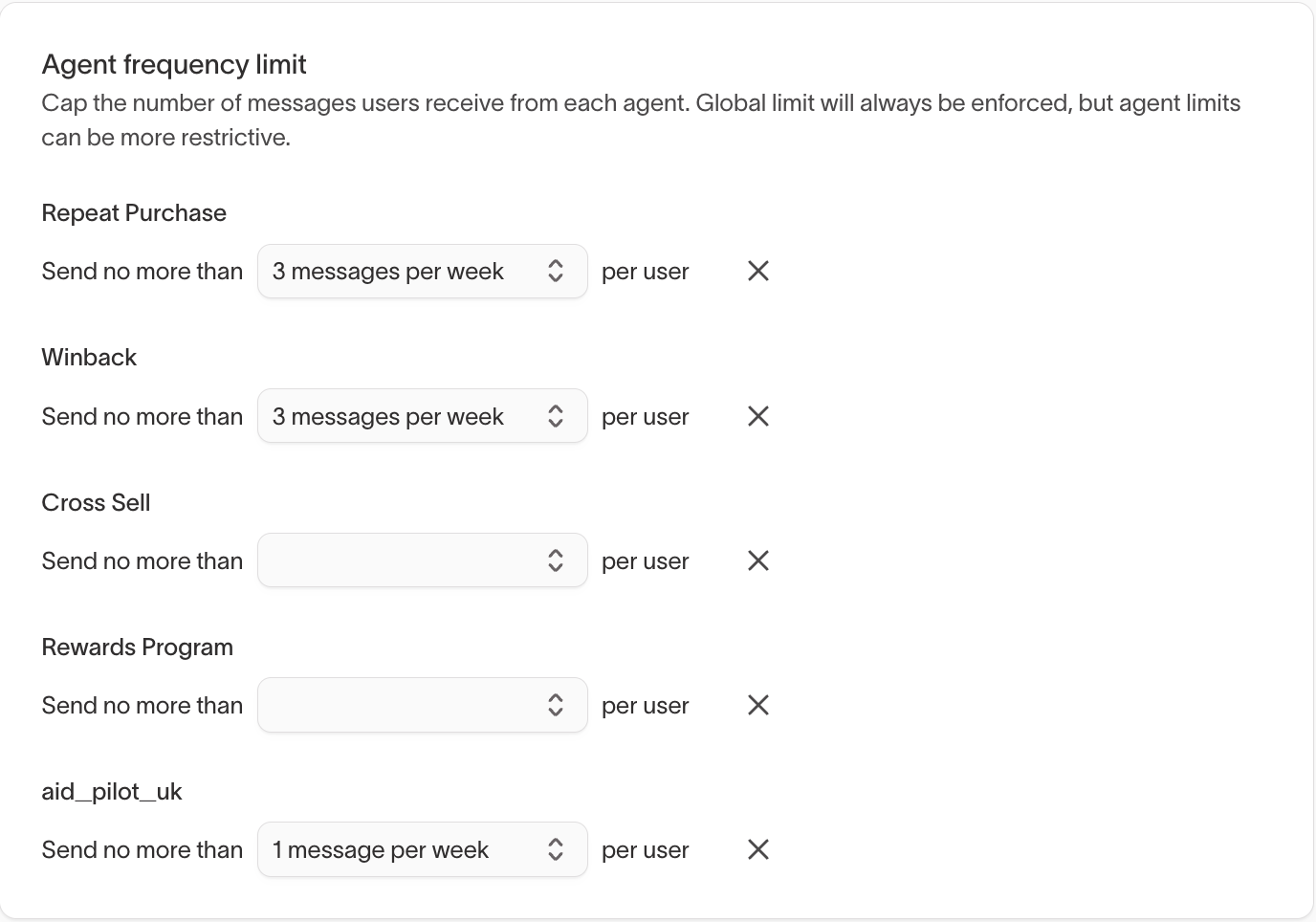
Agent frequency limit
Configure agent frequency limits to apply stricter caps than the global limit.
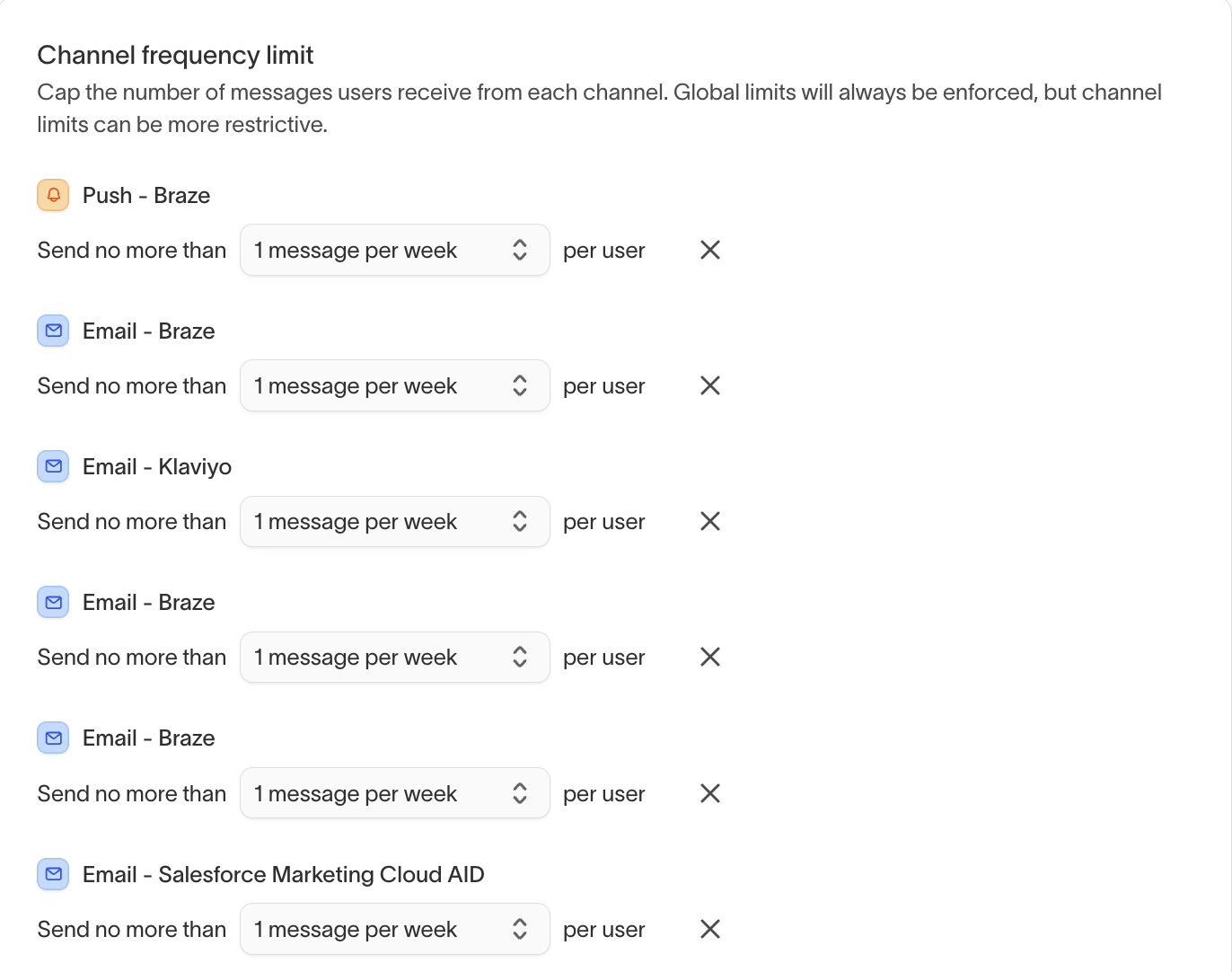
Channel frequency limit
Apply channel frequency limits in addition to global and agent-level frequency limits.
Use channel frequency limits to:
- Enforce channel-specific fatigue controls (for example, stricter limits for SMS)
- Apply consistent limits across all agents using the same channel
- Layer channel limits on top of global and agent-level frequency caps
Channel frequency limits are evaluated in addition to global and agent frequency limits.
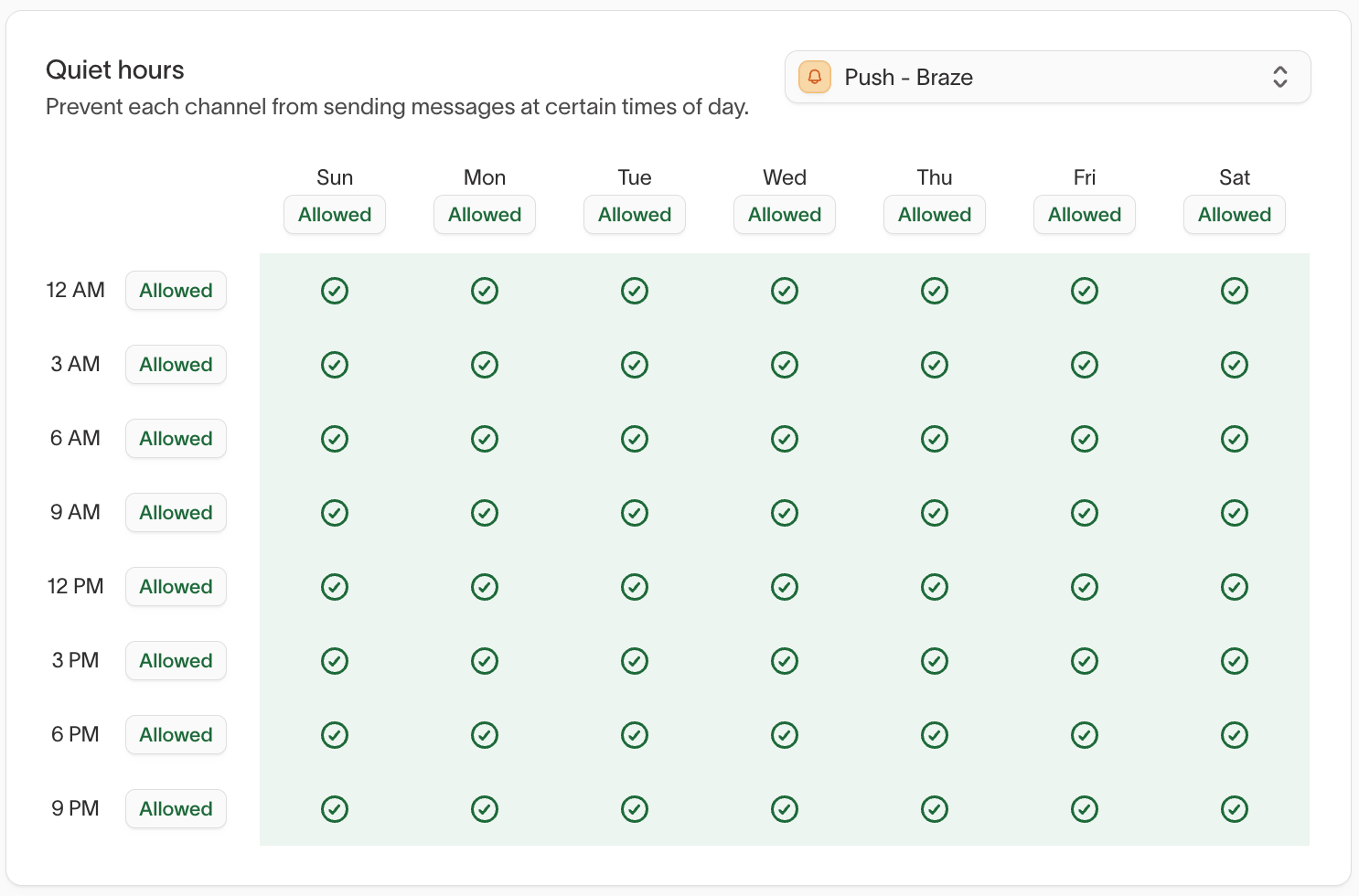
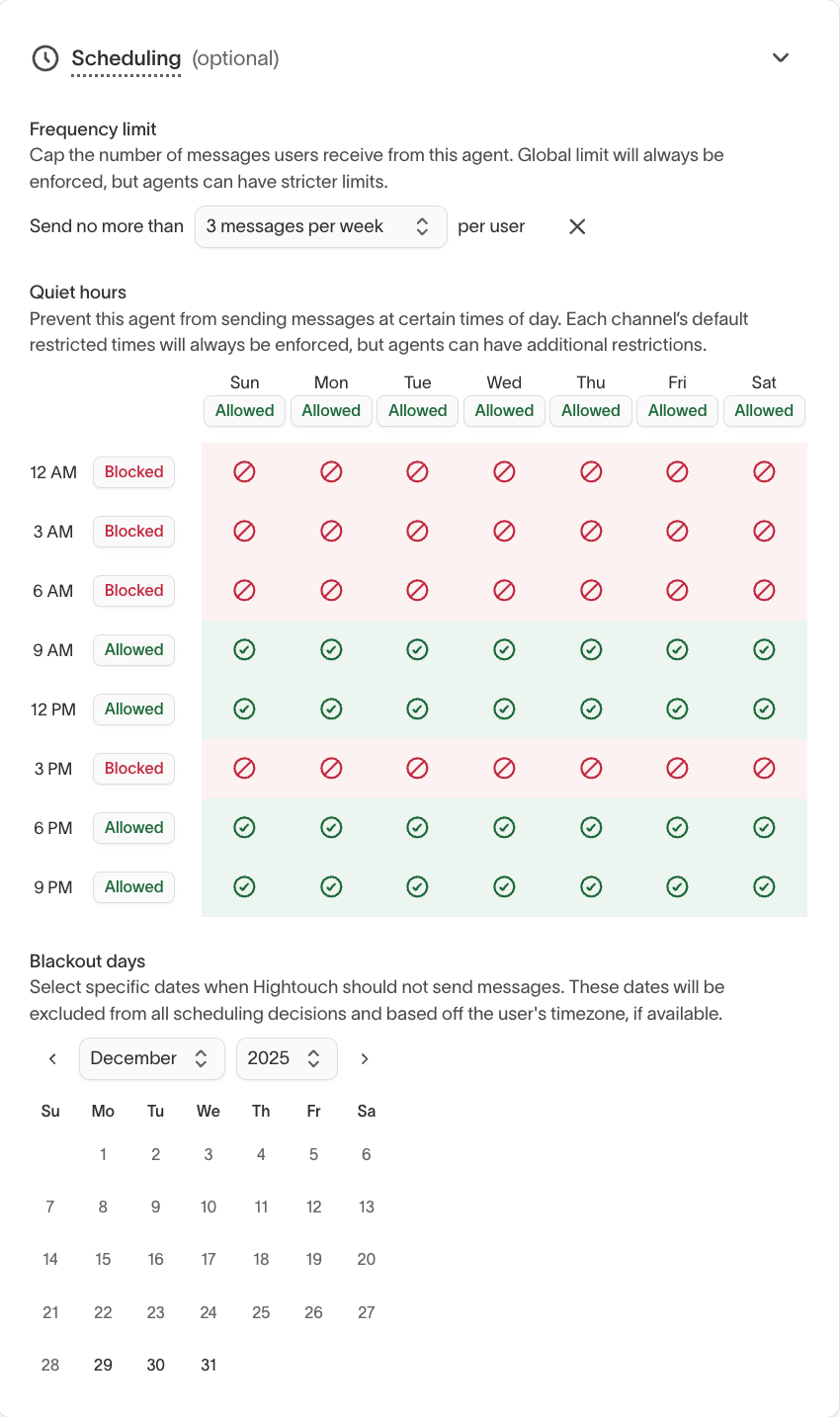
Quiet hours
Quiet hours prevent messages from being sent during restricted times.
They are:
- Configured per channel
- Evaluated using each user’s local time zone
- Applied across all agents and messages using that channel
Agent prioritization
Use agent prioritization to control which agent takes precedence when a user is eligible for multiple agents at the same time.
When overlap occurs, prioritization prevents agents from competing for the same user during the same evaluation window.
When conflicts occur:
- Agents are evaluated based on configured priority
- Higher-priority agents take precedence
- Lower-priority agents may be skipped during the same evaluation window
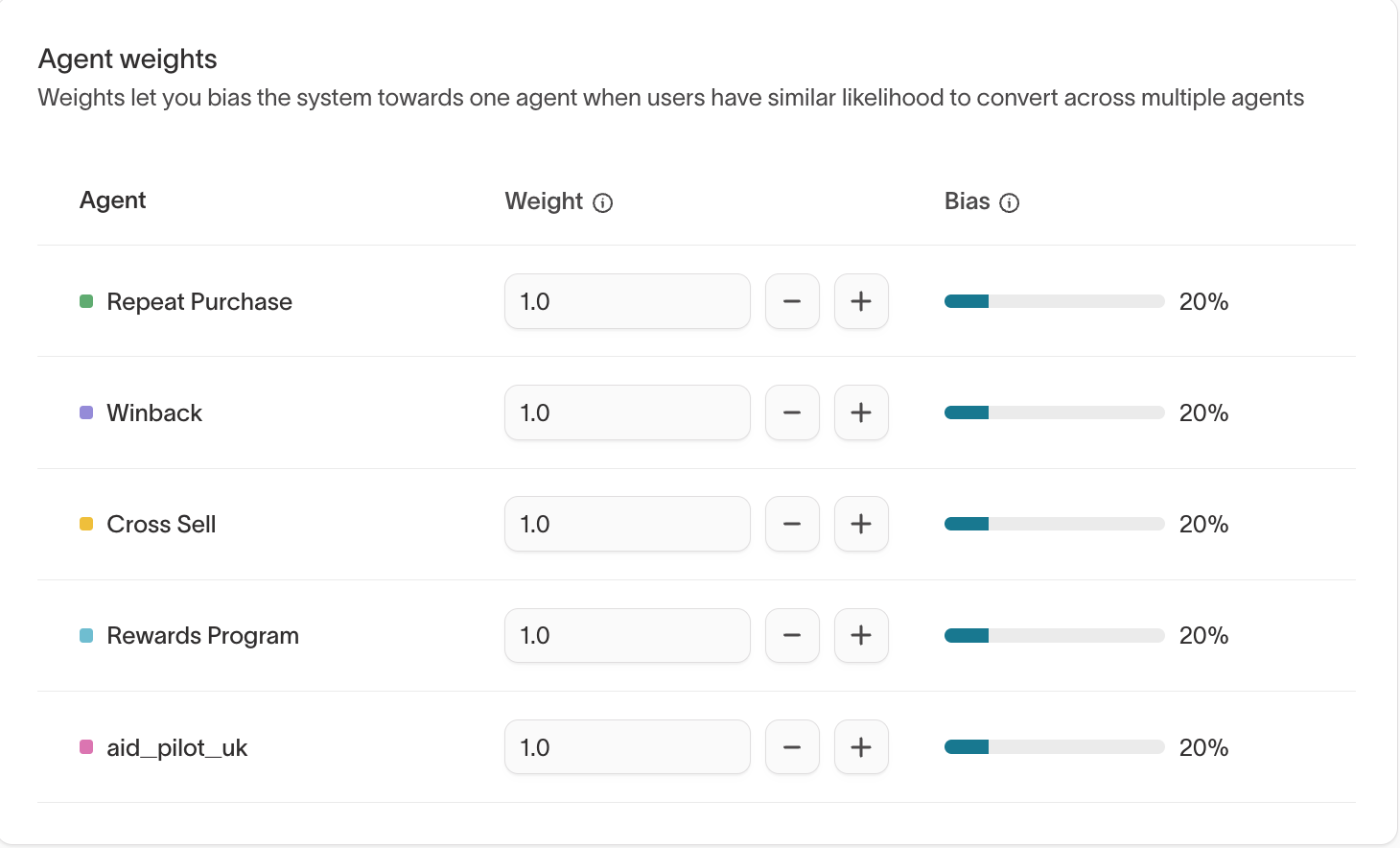
Agent weights
Agent weights indicate the relative priority of each agent when eligibility overlaps.
Adjust weights to bias delivery toward a specific agent when users show similar likelihood to convert across multiple agents.
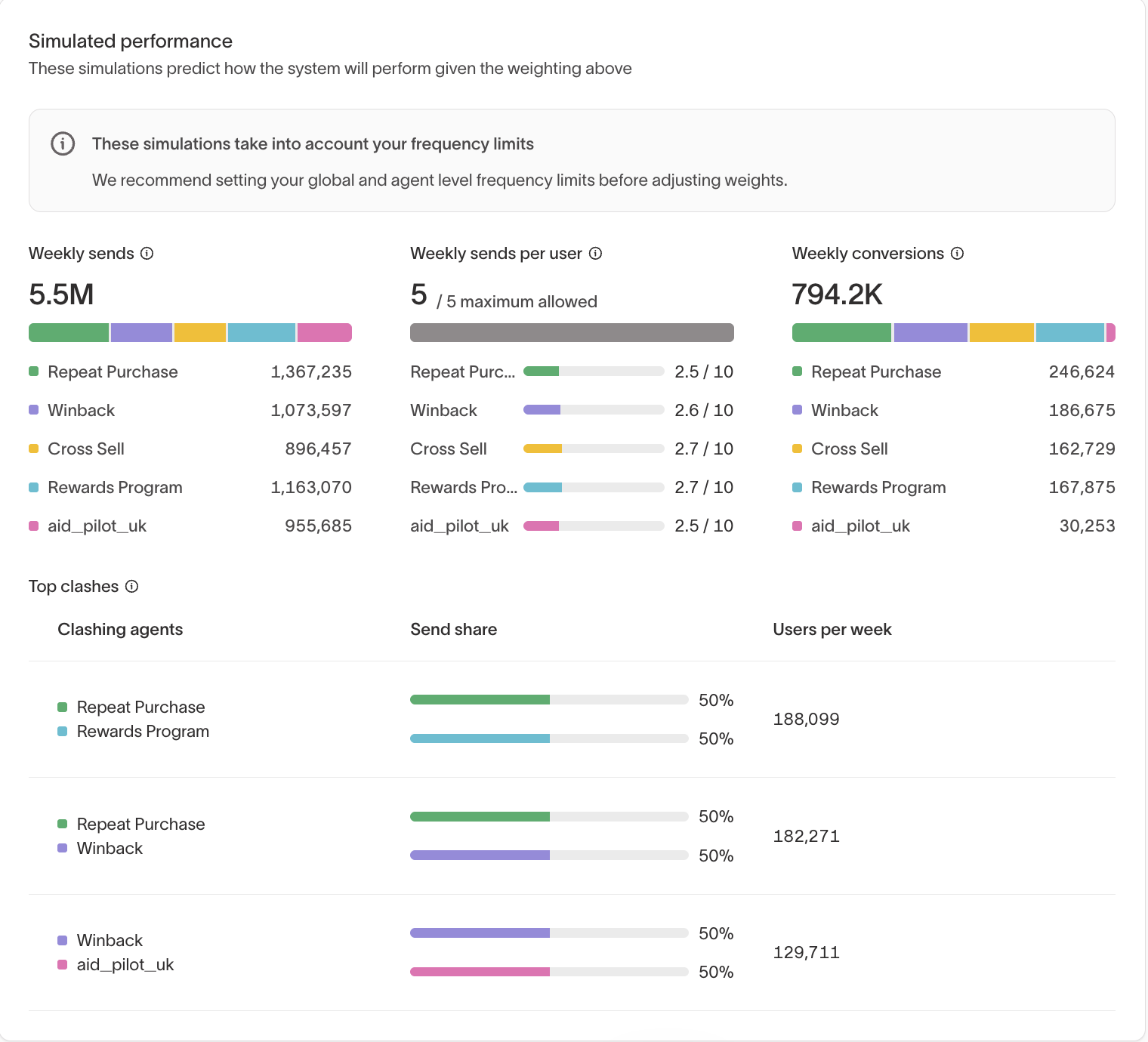
Simulated performance
Simulated performance shows expected agent performance based on historical data.
Use this view to understand how prioritization and weighting decisions may affect outcomes before changing live delivery.
User features
User features define which user attributes are used during decisioning and which of those attributes are available in Insights for analysis.
User features control:
- Which attributes the decision engine can reference when evaluating users and outcomes
- Which attributes are available for breakdowns, comparisons, and analysis in Insights
- How features are described for clarity and interpretability
Use user features to:
- Include only attributes that are relevant to decisioning and measurement
- Exclude noisy or unused fields to keep the decision engine and Insights focused
- Add clear, human-readable descriptions so non-technical users can interpret features correctly
User features are configured per agent, even when agents share the same parent model.

Agent configuration
Agent configuration controls who an agent targets, when it can act, and what it optimizes for.
Agent configuration builds on the global defaults set in workspace configuration and applies only to the selected agent.
To learn more about how agents work overall, see Agents.
How to access agent configuration
- Open the Hightouch app at https://app.hightouch.com.
- Go to AI Decisioning > Agents.
- Select an agent from the list.
- Open the Configuration tab.
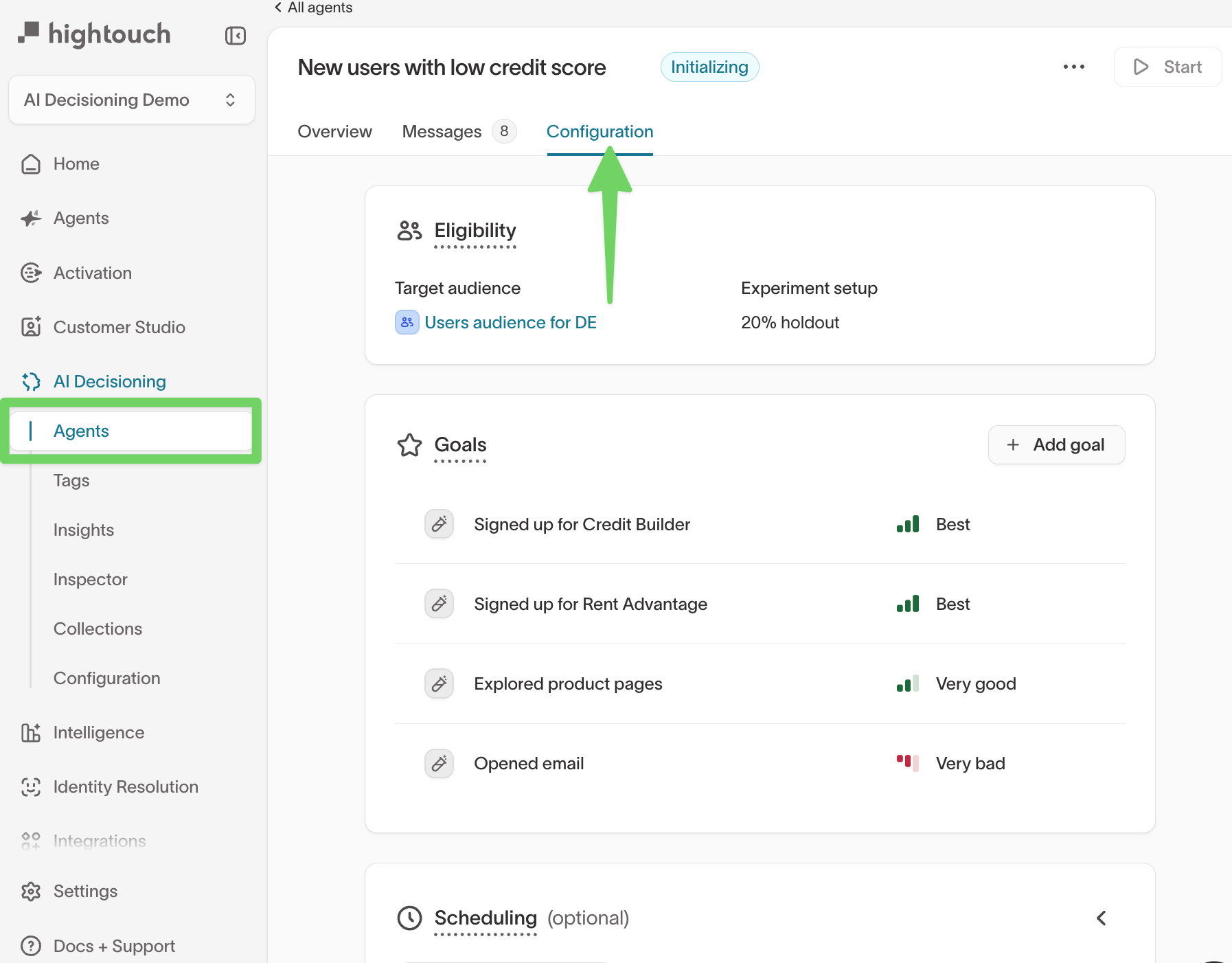
Eligibility
Define which users can enter the agent by selecting a target audience and applying eligibility filters.
Eligibility determines the scope of users the agent can evaluate before considering goals, scheduling, or suppression.
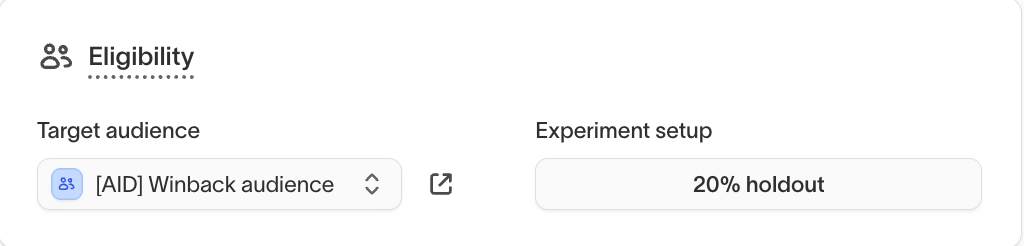
Goals
Select goals to define which outcomes the agent should prioritize when choosing messages.
Goals guide how the agent evaluates success across eligible users and messages.

Scheduling
Configure scheduling to control when the agent is allowed to send messages.
Scheduling settings apply additional constraints on top of workspace-level and channel-level rules.
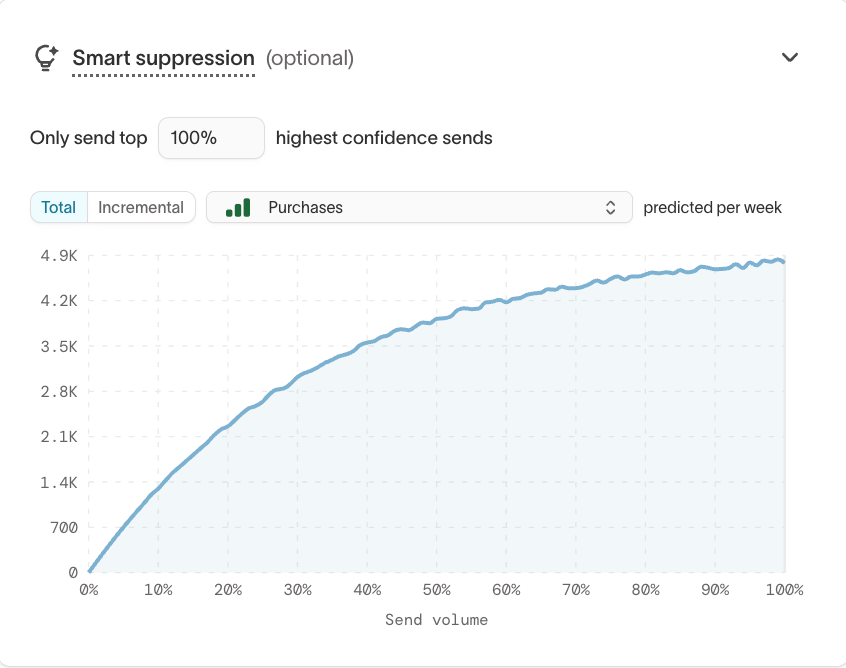
Smart Suppression
Use Smart Suppression to limit sends to users with the highest predicted value.
This setting helps reduce low-impact messaging by focusing delivery on users most likely to respond positively.
To learn more, see Smart suppression.
Advanced
Use advanced settings to support experimentation, exclusions, and specialized agent behavior.
These settings are optional and typically used in more complex setups.
Message configuration
Message configuration controls how individual messages behave once a user is eligible.
How to access message configuration
- Open the Hightouch app at https://app.hightouch.com.
- Go to AI Decisioning > Agents.
- Select an agent, then open the Messages tab.
- Select a message and open its Configuration tab.
Tags
Add tags to describe message intent, tone, or structure and group similar messages for learning and analysis.
Tags help organize messages and provide consistent context when comparing performance across content, variants, and agents.
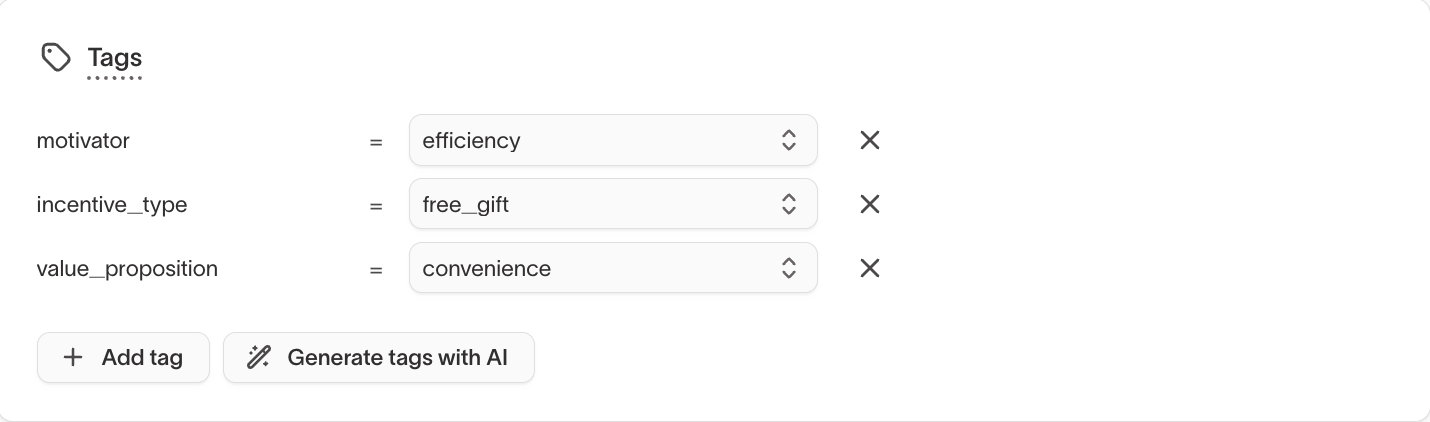
To learn more about defining and managing tags, see Tags.
Goals
Assign message-level goals to measure how individual messages contribute to specific outcomes.
Message goals complement agent-level goals by adding more granular attribution.

Catalog recommendations (collections)
Use catalog recommendations to dynamically include products or content at send time.
You can you tailor messages to each user without creating separate variants.
To learn how to define and manage collections, see Collections.

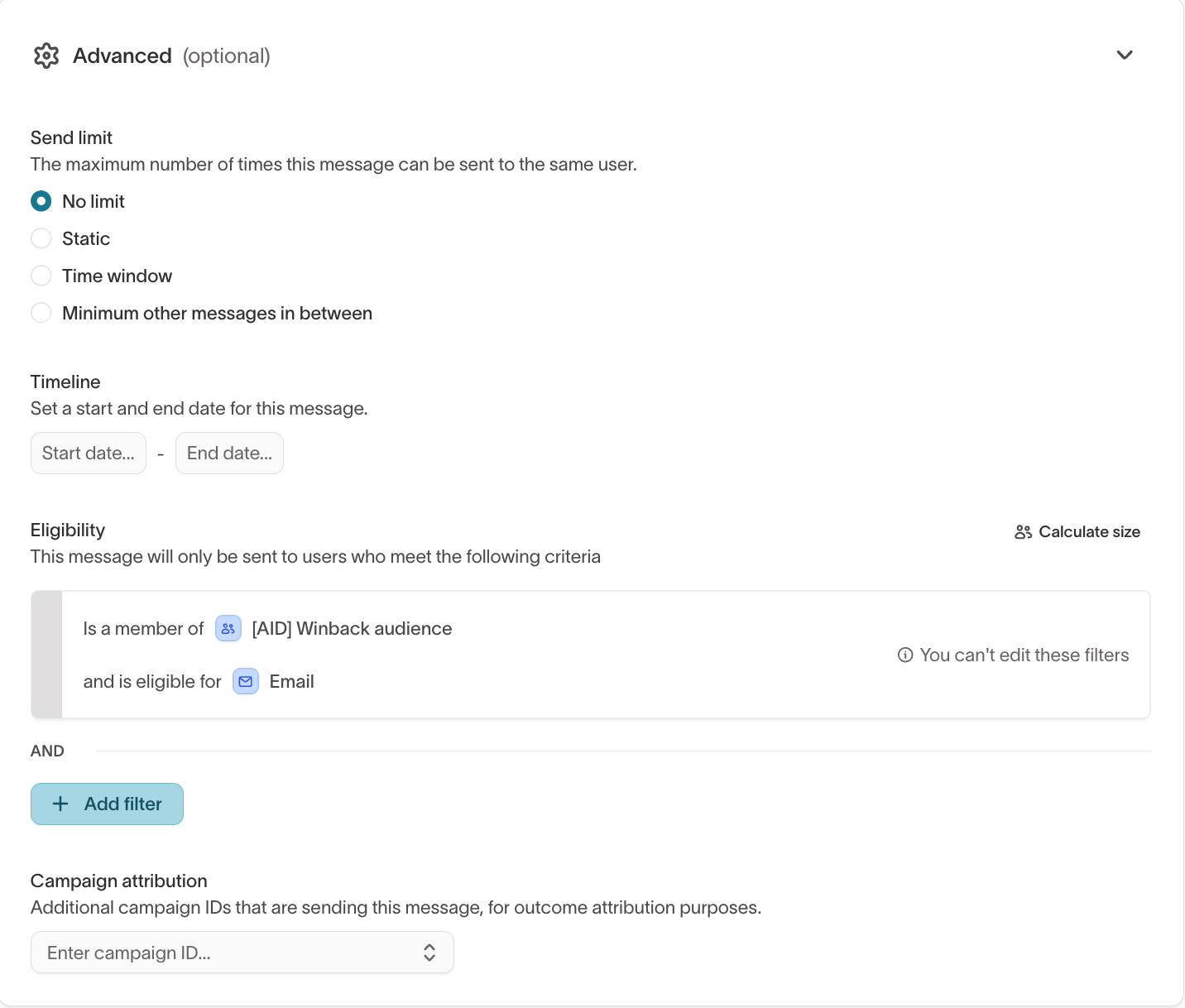
Advanced
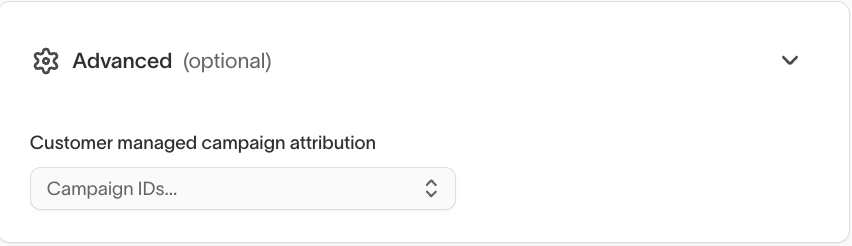
Use advanced message settings to apply additional eligibility filters, configure campaign attribution, and control delivery behavior.
These settings refine how and when a specific message is sent.
What’s next
-
Configure a destination for AI Decisioning: